Technion researchers have developed a new method for the production of hydrogen from water using solar energy. The new method will make it possible to produce the hydrogen in a centralized manner far from the solar farm, cost-effectively, safely and efficiently.
Technion-Israel Institute of Technology researchers have developed a new approach to the production of hydrogen from water using solar energy. In findings published yesterday in Nature Materials, the researchers explain that this approach will make it possible to produce hydrogen in a centralized manner at the point of sale (for example, at a gas station for electric cars fueled by hydrogen) located far from the solar farm. The new technology is expected to significantly reduce the cost of producing the hydrogen and shipping it to the customer.
The study was led by Avigail Landman, a doctoral student in the Nancy & Stephen Grand Technion Energy Program (GTEP), and Dr. Hen Dotan from the Electrochemical Materials & Devices Lab. Ms. Landman is working on her doctorate under the guidance of Prof. Avner Rothschild from the Faculty of Materials Science and Engineering, and Prof. Gideon Grader, Dean of the Faculty of Chemical Engineering.
The study published in Nature Materials was supported by the Israeli Centers of Research Excellence (I-CORE) for Solar Fuel Research (funded by the Planning and Budgeting Committee of the Council for Higher Education of Israel), the Ministry of National Infrastructures, Energy and Water, the European Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Joint Undertaking (FCH JU), the Grand Technion Energy Program (GTEP), donor Ed Satell and the Adelis Foundation.
Hydrogen is considered one of the most promising energy carriers for vehicles and various other uses because of its salient advantages:
- Hydrogen can be produced from water, and therefore production does not depend on access to non-renewable natural resources.
- Using hydrogen fuel would reduce the dependence on fossil fuels such as oil and natural gas, whose availability depends on geographical, political and other factors, and would increase the energy available to the earth’s population.
- Unlike diesel and gasoline engines that emit considerable pollution into the air, the only byproduct of hydrogen fuel utilization is water.
Because of the advantages of hydrogen fuel, many countries – led by Japan, Germany and the United States – are investing vast sums of money in programs for the development of environmentally friendly (“green”) technologies for the production of hydrogen. Most hydrogen is currently produced from natural gas in a process that emits carbon dioxide into the air, but it is also possible to produce hydrogen from water by splitting the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen in a process called electrolysis. However, since electricity production itself is an expensive and polluting process, researchers at the Technion and around the world are developing a photoelectrochemical (PEC) cell that utilizes solar energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen directly, without the need for external power source.
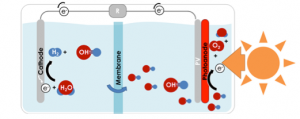
The main challenges in the development of PEC solar farms for the production of hydrogen are 1.) keeping the hydrogen and the oxygen separate from each other, 2.) collecting the hydrogen from millions of PEC cells, and 3.) transporting the hydrogen to the point of sale. The Technion team solved these challenges by developing a new method for PEC water splitting. With this method, the hydrogen and oxygen are formed in two separate cells – one that produces hydrogen, and another that produces oxygen. This is in contrast to the conventional method, in which the hydrogen and oxygen are produced within the same cell, and separated by a thin membrane that prevents them from intermixing and forming a flammable and explosive mixture.
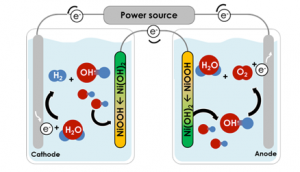
Grâce à la technologie développée au Technion, l’oxygène et l’hydrogène sont produits et stockés dans des cellules complètement séparées. Selon Mme Landman, l’une des électrodes (anode) peut être remplacée par une électrode sensible à la lumière (photo-anode), de sorte que la conversion de l’eau et de l’énergie solaire en hydrogène et en oxygène sera effectuée directement dans chaque compartiment simultanément.
The new process allows geographic separation between the solar farm consisting of millions of PEC cells that produce oxygen exclusively, and the site where the hydrogen is produced in a centralized, cost-effective and efficient manner. They accomplished this with a pair of auxiliary electrodes made of nickel hydroxide, an inexpensive material used in rechargeable batteries, and a metal wire connecting them.
“In the present article, we describe a new method for producing hydrogen through the physical separation of hydrogen production and oxygen production,” says Ms. Landman. “According to our cost estimate, our method could successfully compete with existing water splitting methods and serve as a cheap and safe platform for the production of hydrogen.”
The first diagram shows a conventional PEC device, with a membrane separating the two products (oxygen on the right, hydrogen on the left).
The second diagram shows the technology developed at the Technion: the oxygen and hydrogen are produced and stored in completely separate cells. According to Ms. Landman, one of the electrodes (anode) can be replaced by a light sensitive electrode (photo-anode), so that the conversion of water and solar energy into hydrogen fuel and oxygen will be carried out directly in each compartment simultaneously.
But that’s not all. As stated, the vision of the Technion researchers is geographic separation between the sites where the oxygen and hydrogen are produced: at one site, there will be a solar farm that will collect the sun’s energy and produce oxygen, while hydrogen is produced in a centralized manner at another site, miles away. Thus, instead of transporting compressed hydrogen from the production site to the sales point, it will only be necessary to swap the auxiliary electrodes between the two sites. Economic calculations performed in collaboration with research fellows from Evonik Creavis GmbH and the Institute of Solar Research at the German Aerospace Center (DLR), indicate the potential for significant savings in the setup and operating costs of hydrogen production.
In October, Ms. Landman won first place in the energy category in the Three Minute Thesis (3MT) competition held in Australia. At the competition, held on the initiative of the University of Queensland, participants are required to present groundbreaking research in just three minutes. In her lecture, presented in the following link, Ms. Landman briefly presents the current study: https://player.vimeo.com/video/187919440
The method developed at the Technion for separating hydrogen production and oxygen production was the basis for the development of new two-stage electrolysis technology. This technology, which was developed by Dr. Hen Dotan, enables hydrogen production at high pressure and with unprecedented efficiency, thus significantly reducing hydrogen production costs. The new technology is now in its pre-industrial development stage.
Publication in Nature Materials